The following TIMELINE of Persia and Iran with Maps will examine 3,000 years of the history of Persia/Iran. The chronology shows the powers that controlled and conquered the region; as well as how Iran came to be what it is in the world – geographically and politically.
Persia / Iran’s Geography and Ancient history
Like most nations on earth, the land of the country of Iran has been conquered by many empires – the most significant that of Persia. In 1959, the government under Mohammad Pahlavi stated that the nation was officially ‘Persia’ or ‘Iran,’ but today it is officially the Islamic Republic of Iran. Iran comes from Avesta (Zoroastrianism), Sanskrit, Persian and Parthian from which is Aryan, meaning land of Aryans – of kinsmen, of nobles and or kings. The land of king Aryanman, who lived about 1000 BC during the time of King David of Israel. Persia likely comes from the Arabic and Farsi word fars – horsemen (the horse people). Modern Persian and Arabic firdaus translated through the Greek to refer to ‘paradise’ or land of plenty.
All the people and nations of the world came from the Fertile Crescent. The descendants of Adam and of Noah came from Mesopotamia – the lands between the rivers (Tigris & Euphrates).
![babylon[1].jpg](https://thetruthsource.files.wordpress.com/2019/05/babylon1-1.jpg?w=616)

The families of the sons of Noah migrated, multiplied and created settlements before 2,000 BC. Genesis chapter 10 tells of the descendants of Shem, Ham and Japheth; including how from them came the “first centers of Nimrod’s kingdoms: Babylon, Ur, Akkad and Kalneh. As well as Assyria, where Nimrod (great-grandson of Noah) built Nineveh and Calah. (Gen. 10).”
Note that the Babylonian text ‘The Epic of Galgamesh’ (written c.1700-2,000 BC) and the Hebrew Old Testament (oral tradition from c. 2,100 BC) telling of Noah and the Flood describe the account with about 20 main points in common; where the Quran/Koran’s version (written after 630 AD) is significantly different lacking in numerous details and replacing certain events, including the course and death of one of Noah’s sons.
![Noah-Sons-Fig5-Ham-800x400[1].jpg](https://thetruthsource.files.wordpress.com/2019/05/noah-sons-fig5-ham-800x4001-1.jpg?w=616)
Abraham, ten generations from Noah, was the son of Terah. Terah was from the land of Ur; and Abram was brought out from the land of Ur or the Chaldeans to Canaan – to Palestine and Israel. This was about 1700 BC; about the time of China’s 1st dynasty, Xia; before India’s dynasties; during the time of Egypt’s Middle Kingdom.
see: Genesis Chronology
About this time according to Genesis, ‘the whole world had one language’ and many had come together in Shinar or Babylonia and built a tower reaching into the heavens. The tower was destroyed and the people were scattered and the languages became confused or Babel. (Genesis 11)
Babylon

Hammurabi is said to be the sixth king of the first Babylonian Dynasty. He conquered Elam (ancient pre-Iranian lands). The Code of Hammurabi is in the Louvre Museum in Paris. Through the population of the world was only in the millions, the Babylonians became a great Empire and ruled for centuries.
The prophet Daniel, after the time of Egypt’s greatest, prophesied of four great empires: Babylonian Empire (‘a beast like a lion with eagle’s wings’); the Medo-Persian Empire; the coming Greek Empire; and what would be the Roman Empire. (Daniel chapters 2 & 7)

The winged lions of Babylon from the ‘Processional Way’ and the Ishtar gate (c. 600 BC) can be seen in various museums today.
The Prophet Daniel told king Belshazzar, grandson of king Nebuchadnezzar of Babylon, who conquered the Jews and took the treasuries from the Temple in Jerusalem, ‘You have been Numbered, weighed and divided… your kingdom will be divided and given to the Medes and the Persians… Darius the Mede took over the kingdom (Daniel chapter 5).’

The Persians (and Medes)
Darius the Mede, was the general or king of the Medes who entered Babylon c. 539 BC at the time when king Cyrus the Great (of Anshan, Iran) conquered Babylon. Cyrus reign from c. 559 to 530 BC. Cyrus conquered the Median Empire and became King of Babylon, king of Media, king of Persia, king of the world. Through marriages and war, the Bactrians, Parthians and Saka came under the Persian kings.


The Greeks
By 330 BC, king Alexander the Great of Greece had conquered Egypt, Babylon, Assyria and most of the Persian Empire and reached into India. At age 32 (c. 323 BC), Alexander – King of Macedonia, Pharaoh of Egypt, King of Persia, died in the palace of Nebuchadnezzar II.
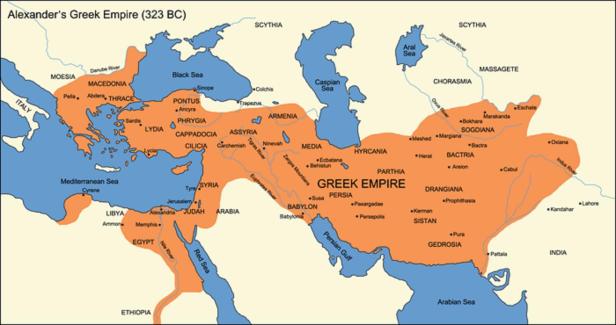
After his death, Alexander’s Empire was divided into four kingdoms, and taken over by his generals and relatives. General Seleucus I Nicator ruled over part of Anatolia, as well as Babylonia, Mesopotamia, Persia and the Levant. His capitals were Seleucia is now Baghdad, Iraq; and Antioch of Syria.

Roman Empire

The Seleucid Empire fell to the Romans and their allies. The last of the Seleucid kings was defeated by the Roman general Pompey in 63 BC. This was about a century before the Romans under Titus would destroy the Temple in Jerusalem (70 AD). The Roman Empire was said to have reached its greatest extent in 117 AD during the reign of Emperor Hadrian (117-138 AD). Not long after the Parthian Empire was established. The Parthian kings ruled from about 247 BC to 224 AD when after defeat they were dissolved into the Sasssanid Empire. At that time there people had little religion – primarily cults, polytheistic beliefs and non-religion.

Byzantine Empire in the West / Sasanian Empire in the East

The Sasanian Empire lasted from about 224 to 651. It was the Empire of Iranians and the last kingdom of the Persian Empire before the invention of Islam; and the rise of the Muslims. The Sasanian Empire, founded by Ardashir I, stood alongside of the Roman-Byzantine Empire.
Constantine the Great became Emperor of the Roman Empire in 306. He was the first Roman Emperor to convert to Christianity. In 324 he moved his capital to Byzantium, which became Constantinople around 330, until 1453 when the Ottoman Turks (Muslims) conquered the city and renamed it Istanbul.


Muhammad and the Rise of Islam
Between about 622 and 632, Muhammad, the founder of Islam, converted men from the tribes in Medina; and he developed an alliance with certain tribes. He and his followers raid caravans which provided resources to feed and build his army. By 623, Muhammad had a few hundred followers that fought for him. By 630, the Muslims had control of Mecca and their religion was being spread to the people and their captives. Muhammad died in 632, leaving a quasi-Christian religion called Islam; which contain many of the Biblical stories and figures; but changed much of the Hebrew and Christian texts in the Muslim’s Koran (Quran).
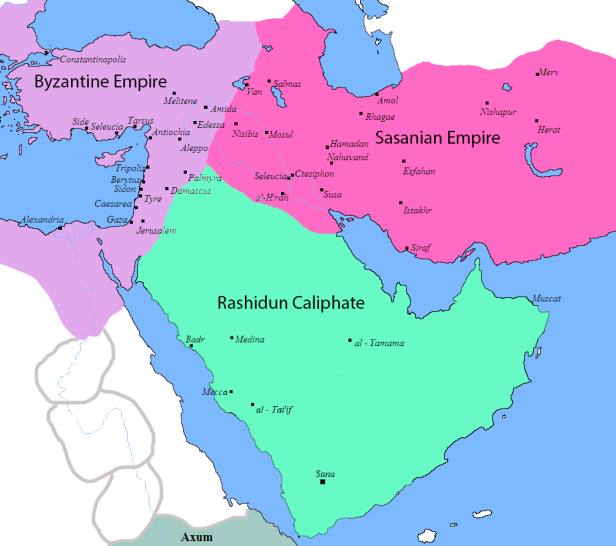
By his death the where over 12,000 Muslims warriors and they controlled much of Arabia. The Muslims split after the death of Muhammad, most (80+%) following Sunni Islam in which it is taught Muhammad did not leave a successor and his father-in-law, Abu Bakr is viewed as the first caliph. The Shia Muslims believed Muhammad made his son-in-law Ali ibn Abi Talib his successor. From that time there were times of disagreement and tension between the Sunnis and the Shias. From the death of Muhammad to about 651 and 661, Muslim lands where mainly under the control of the Sasanian Empire and Rashidun Caliphate (first major Caliphate). Nevertheless, within a century – by 740 AD – the Muslims primarily under the Umayyad caliphs (leaders) control lands from North west Africa and Spain, along the African coast, through Egypt and Arabia to Afghanistan; which of course included Syria, Iraq and Iran.
The Sasanian Empire was succeeded by the Qarinvand Dynasty (who’s main religion was Zoroastrianism). Many were converted to Islam. There Dynasty ruled much of northern Iran from 550 to about 1050. During that time there were other Dynasties or families and rulers that reigned over various parts of Iran, such as the Rashidun Caliphate, the Zarmihrids, the Abbasid Caliphate and the Bavand Dynasty was ruled from about 651 to 1349. The Bavandids were originally Zoroastrians and converted to Sunni Islam and many to Twelver Shia Islam.

The Ghaznavid Dynasty lasted from about 977 to 1186 and at their greatest extended ruled over most of Iran, Afghanistan and what is now other modern nations. The Ghaznavid were of Turkic Mamluk origin and converted to Sunni Islam.



Though ruled by Muslims, the lands were divided between different tribes and caliphs.
![rul-jus-islamic-period-13[1].jpg](https://thetruthsource.files.wordpress.com/2019/05/rul-jus-islamic-period-131-1.jpg?w=616)
![Khwarezmian_Empire_1190_-_1220_(AD)[1].png](https://thetruthsource.files.wordpress.com/2019/05/khwarezmian_empire_1190_-_1220_ad1.png?w=637&h=440)
Khwarizm Shah or Khwarzmid Dynasty ruled over 100 years until the Mongol invasion.

The Mongol Empire and the Khanates

Genghis Khan, the founder of the Mongol Empire, reigned from about 1206 to his death in 1227. He had over a dozen wives and concubines. Likewise, many of his sons had wives and consorts. Kublai Khan was the 5th Khagan of the Mongol Empire and 1st Emperor of the Yuan Dynasty of China. He was a grandson of Genghis and widely extended the Mongol Empire during his reign of 34 years (1260 to 1294).

In 1260, the Muslim Mamlukes of Egypt, lead by Sultan Qutuz, defeated the Mongols in Galilee. Galilee had a majority Jewish population during the seventh century, but was conquered by Arab Caliphates about 638 and later controlled by the Muslim Shia Fatimids in the 10th century and would fall under various Muslim caliphs and the Ottoman empire until post-War World II.
Turks Mongols and the rise of the Safavid
From about 1400 to 1600, Iran was ruled by Turko-Mongol Dynasties. The main ones were the Jalayirids (Iraq and northwestern Iran), Timurids (Fars region; Timur Empire), Qara Quyunlu and Aq Quyunlu. However, by the mid-1500s, the Safavids control the vast amount of Iran.
Ottoman Empire and Persian/Iranian Dynasties

In 1514, the Ottoman Turks took part of eastern Anatolia from the Shah Isma’il. Numerous Ottoman-Safavid conflicts and battles followed until the Ottomans were forced out of Iran and Transcaucasia. In 1597, Shah Abbas (son of Shah Mohammad Khodabanda, who he overthrew) moved his capital from Qazvin to Isfahan. Abbas reigned until his death in 1629 when he was succeeded by Sam Mirza Shah Safi who was only age 18 but ruthless in many ways. He was a grandson of Abbas and was succeeded by his son Shah Abbas II who ruled until 1642. Then his son, Safi II ruled until 1694 when the 9th Safavid Shah (king) of Iran began to rule.

![Islamic_States_1620_lg[1].jpg](https://thetruthsource.files.wordpress.com/2019/05/islamic_states_1620_lg1.jpg?w=616)
In 1600, the Muslim Ottoman Turks and the Muslims of the Safavid controlled most of the Middle East and parts of North Africa. During the Great Turkish War of 1683 to 1697 the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the Holy League alliance under the Roman Catholic Church and Pope Innocent XI. Most of Hungary was given back to the Christian leaders after the Ottomans signed the Treaty of Passarowitz in 1718. This also increased Poland’s territory and the Austrian State of the Habsburgs.

The Russian Empire, Ottoman Turks and the Islamic Khanates
Sultan Husayn reigned until 1722 by which time his control was lost to several revolts and more so during the Russo-Persian War against Peter the Great, Tsar of the Russian Empire. And seeing opportunity the Ottoman-Persian War followed lasting 1730 to 1735. The Crimean Khanate of the Ottoman Empire (1441 to 1783) fought against both the Persian Muslim of Iran and the Russians in the Russo-Turkish War (1735-1739). They had some years without much struggle, but many were filled with tensions, revolts and war. And again, during the reign of Catherine II of Russia, the Russo-Turkish War of 1768 to 1774 took place (ending about 2 years before the Colonies of America declared independence from Britain.


The Safavid Empire held its control over the Persian region east of the Tigris River for over 230 years. Their kings ruled Iran from about 1500 until about 1736 when the Hotaki (Afghans) and Afsharid Dynasty (Turkic Afshar) took over; and when land was lost to the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire.

The Qājār Dynasty (a Turkic Qajar tribe) ruled Qajar Iran – the Sublime State of Persia ruled over Iran from about 1789 to 1925. Note in 1789, U.S. President George Washington was in his first year as president of the United States. After the leader of the Zand dynasty eliminated all his rivals; he was crowned as shah or emperor and then was assassinated in 1797 and succeeded by his nephew who was defeated by Russia in two wars between 1804 and 1828. This son Naser od-Din reign for almost 50 years until 1896; while dealing with British and Russia politics. The capital of the Qājār Dynasty was Tehran and the primarily religion was Shia Islam under a Monarchy. The last Shah was Ahmad and from 1906 to his end in 1925 there were about 20 Prime Ministers.

British Influence, Oil, World Wars and Iran
During the late 19th struggles continued such as the Persian Constitutional Revolution. In 1870 the Great Persian Famine sweep the region and as many as 2 million people died. But soon the land would reveal something that would cause more deaths – oil. In 1906, petroleum was discovered by the British in Khuzestan. The British Empire set up the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company, which is now called British Petroleum (BP).

The first Parliament or Majlis convened that same year, 1906. In 1907, the great world powers were striving to get their hands into the oil region. The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 resulted in Persia begin divided into “Spheres of Influence.” By 1910, much of Asia, as South America and Africa, was under colonial controls of the major European world powers, as well as Russian and Japan.

During World War I (1914 – 1918), Persia was occupied and fought over by British (with British Indian support), Ottoman (with German support) and Russian (Cossack and Caucasus support) forces. After WWI, in 1919, the Russian Revolution began and forced Russia to withdraw its interest in Persia. This allowed the British to attempt to dominate the region; but their Protectorate status quickly failed and gave way to the rise of Reza Khan – Shah Pahlavi.
By 1925, the Pahlavi Empire was established and would last until 1979. During that time there were only two Shahs – Reza and Mohammad Reza. In 1978, the Iranian Revolution or Islamic Revolution began which resulted in the end of the monarchy and the establishment of the Islamic Republic of Iran. In 1979 the monarchy was dissolved, and the Shah left in exile (ending up in the United States which angered many in Iran) and new type of anti-Western Imperialism Theocracy – Quasi Monarchy arose.
Ayatollah (Sayyid Ruhollah) Khomeini became the First Supreme Leader – the Grand Ayatollah and Iman– of Iran from 1979 to 1989. Under him was the President and Prime Minister. The environment and time opened the way for the Iran-Iraq War, the 1979 Oil Crisis and the Iran Hostage Crisis; as well as a volatile region.
